Thin layers of polymer are applied to either flat surfaces or irregular objects to create polymer coatings. Polymeric coatings can be attractive, protective, or useful (adhesives, photographic films, etc.). They are also used to alter surfaces (paper coatings, hydrophobic coatings). Read More…
Precision Dip Coating provides dip coating services for the manufacture of soft plastic parts such as cap plugs. hand grips, and more. Decorative and protective, our services are very cost effective and we have a proven track record for on time delivery and precise manufacturing. We can match any color you need, and offer services such as assembly, die cutting, packaging, and decorating.
Carlisle Plastics is a dip molding plastics manufacturer offering end caps, plastisol paint masks, thread protectors, tube closures, protective caps and decorative caps.

At Production Sciences, Inc., we pride ourselves on being pioneers in the realm of dip-molded plastics, sculpting a legacy of innovation and excellence that spans decades. As a collective force, we embody a commitment to precision, creativity, and unwavering quality in the realm of plastic manufacturing.

Innovative Coatings is a manufacturer of plastisol dip molding and fluidized bed powder coatings of epoxy, polyolefins, nylon and vinyl. Our dip coatings are of FDA-approved and biomedical grades.
More Polymer Coating Companies
What is Polymer Coating?
Although polymeric coatings are mostly made of organic materials, they can also contain metal or ceramic particles to improve their performance, durability, or attractiveness. Because polymer coating solutions are frequently expensive, coating techniques are used to create a polymer layer as quickly and thinly as feasible.
Polymeric coatings typically have a thickness of 1 to 100 µ. Polymeric coatings are applied using various coating techniques according to the desired coating thickness, the liquid's rheology, and the speed of the web.
Also common are multilayer coatings. Polymer solutions, monomer liquids, and polymer polymer latexes are the three distinct starting liquid types that can be utilized to get this result, even though all polymeric coatings are intended to be impenetrable, uniform thin films of polymer when dry.

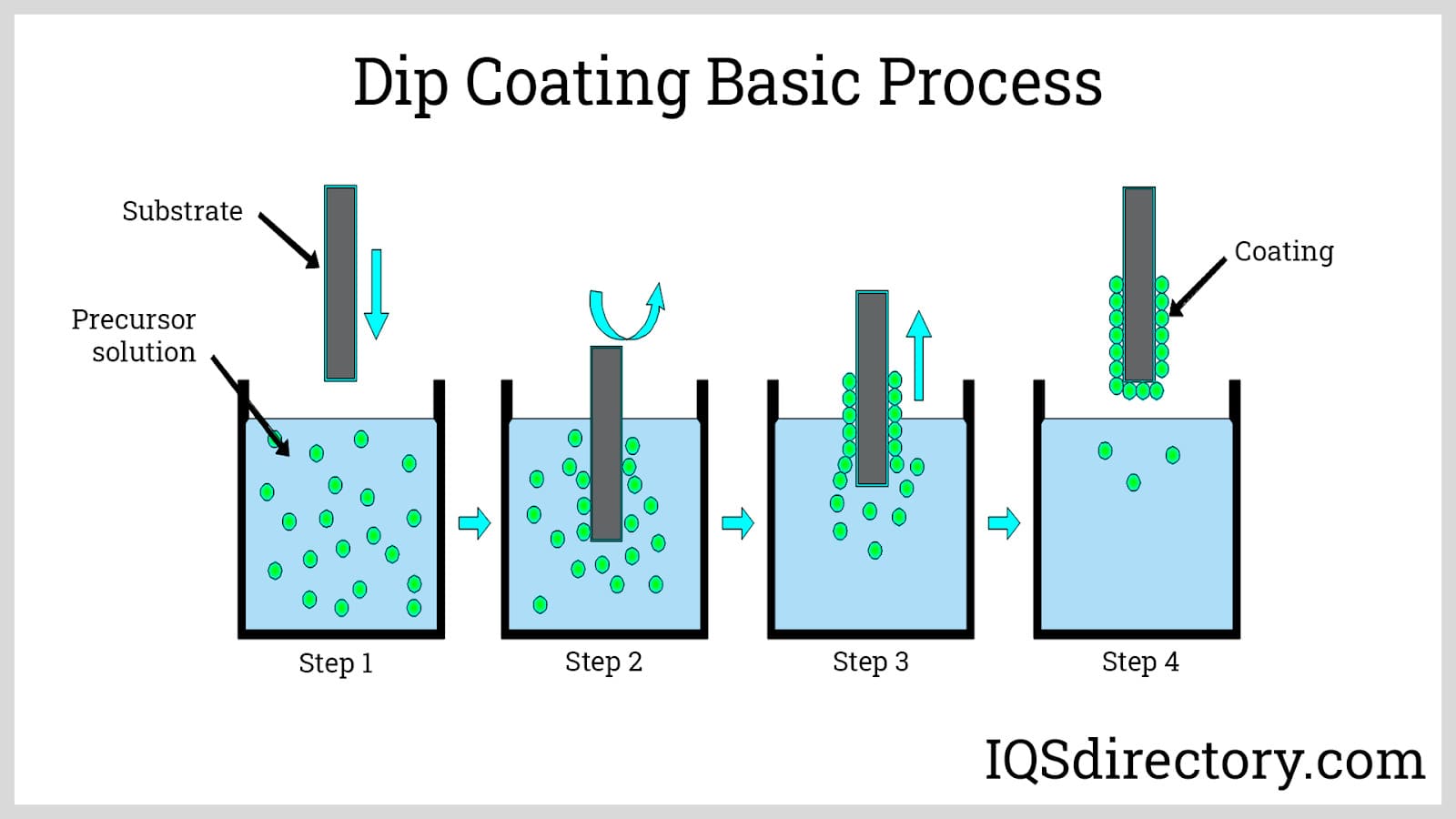
Dip Coating of Polymers
The process of dip coating also known as immersion coating, produces polymer coatings. In the process of dip coating, a substrate is submerged into a tank filled with a liquid polymer coating material, removed, and left to drain. The three steps of the process are immersion, dwell time, and withdrawal.
During immersion, the substrate is continuously submerged in the liquid polymer. The substrate must remain still and completely submerged during the dwelling stage for the liquid polymer to adhere to the substrate and gel. The substrate is then removed in the withdrawal stage at a steady pace.
The thickness of the polymer coating depends on how rapidly the substrate is taken from the tank. Hot dip and cold dip coating are the two types of dip coating techniques. Most polymer coating applications use the hot dip coating method, which is far more widespread. In this procedure, heated and primed substrates are dipped into the polymer from an overhead rack while the polymer material is retained in a liquid state.
Since most polymers benefit from some heat processing, the polymer on the substrate is heated. Therefore, cold dip coating is less prevalent and is mostly utilized for thin polymer coatings. In this method, the object is placed in the heated chamber for final fusion after being dipped unheated in a liquid polymer.

Materials Used for Polymeric Coating
Compared to coatings for aesthetic purposes, corrosion-resistant polymeric coatings are typically harder and placed in heavier films. Polymeric coatings must stick firmly to the substrate and must not crack or deteriorate when exposed to heat, moisture, salt, or chemicals. Because of growing worries about heavy metals and the environment, polymeric coatings are replacing chrome and cadmium coatings.

Hydrophobic surfaces can be made using specific polymers in coatings, and diverse substances like adhesives, rubber, and synthetic materials can be successfully prevented from adhering to these surfaces. In addition, by lowering the contact area, the intentional modification of the surface structure employing specified roughness profiles improves the non-stick effect (e.g., Teflon coating, PTFE, and PFA).
Among the polymeric coatings are:
- Acrylics and alkyds are frequently used for industrial products and farm equipment that need superior corrosion protection at a reasonable price.
- Conveyor equipment, aircraft, radomes, tugboats, road-building equipment, and motorbike parts are all made of polyurethane. On railroad hopper cars, urethane coatings with abrasion resistance are applied. Sandblasting cabinets and slurry pipes are lined.
- Nylon 11 - Offers a pleasing look and defense against chemicals, abrasion, and impact.
The viscosity behavior of a new class of coating, an alloy of fluoropolymers and other resins, differs from that of the earlier organics. Fastener-class coating resins exhibit a significant decline in viscosity with increasing film shear.
Advantages of Polymer Coating
- Adhesion is the bonding of different surfaces.
- The capacity of a liquid to retain contact with a solid surface is known as wettability.
- Corrosion resistance: Some metals are more resistant to corrosion than others. Corrosion is the process through which refined metal transforms into a chemically stable form. Applying polymer paints or coatings will stop metals from oxidizing and corroding.
- Wear resistance: The rate of wear varies with its stage (early, middle, or old). Chemical reactions between the worn material and the corroding medium are the primary cause of wear resistance.
Choosing the Right Polymer Coating Company
For the most beneficial outcome when selecting a polymer coating company, it is important to compare several companies using our directory of polymer coating businesses. Each polymer coating company has a business profile page highlighting their areas of experience and capabilities, along with a contact form to directly communicate with the business for more information or request a quote. Review each polymer coating business website using our patented website previewer for an idea of what each company specializes in. Then, use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple businesses with the same form.





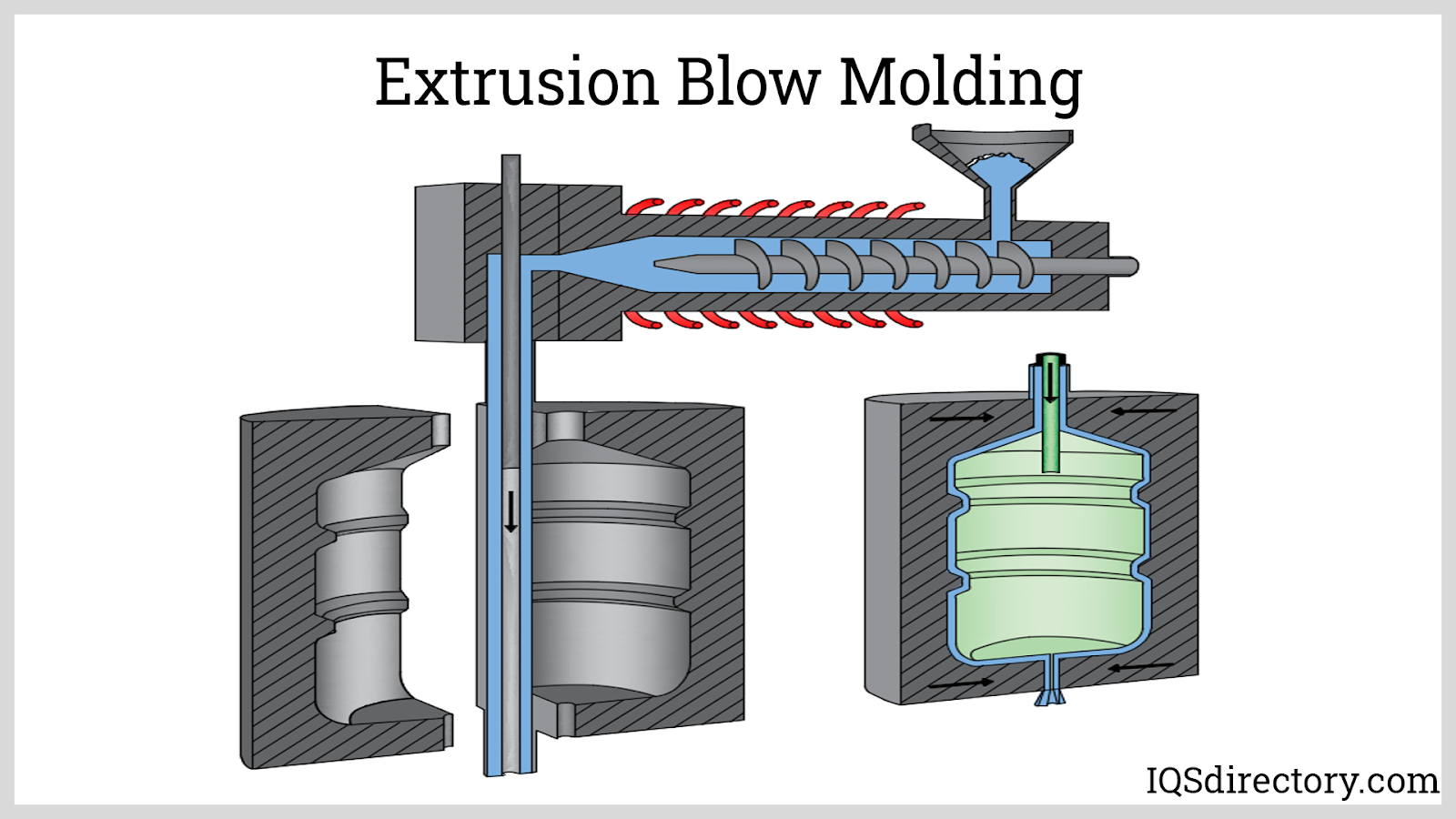

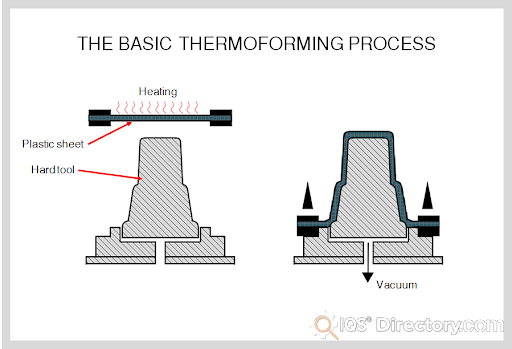
 Fiberglass Fabricators
Fiberglass Fabricators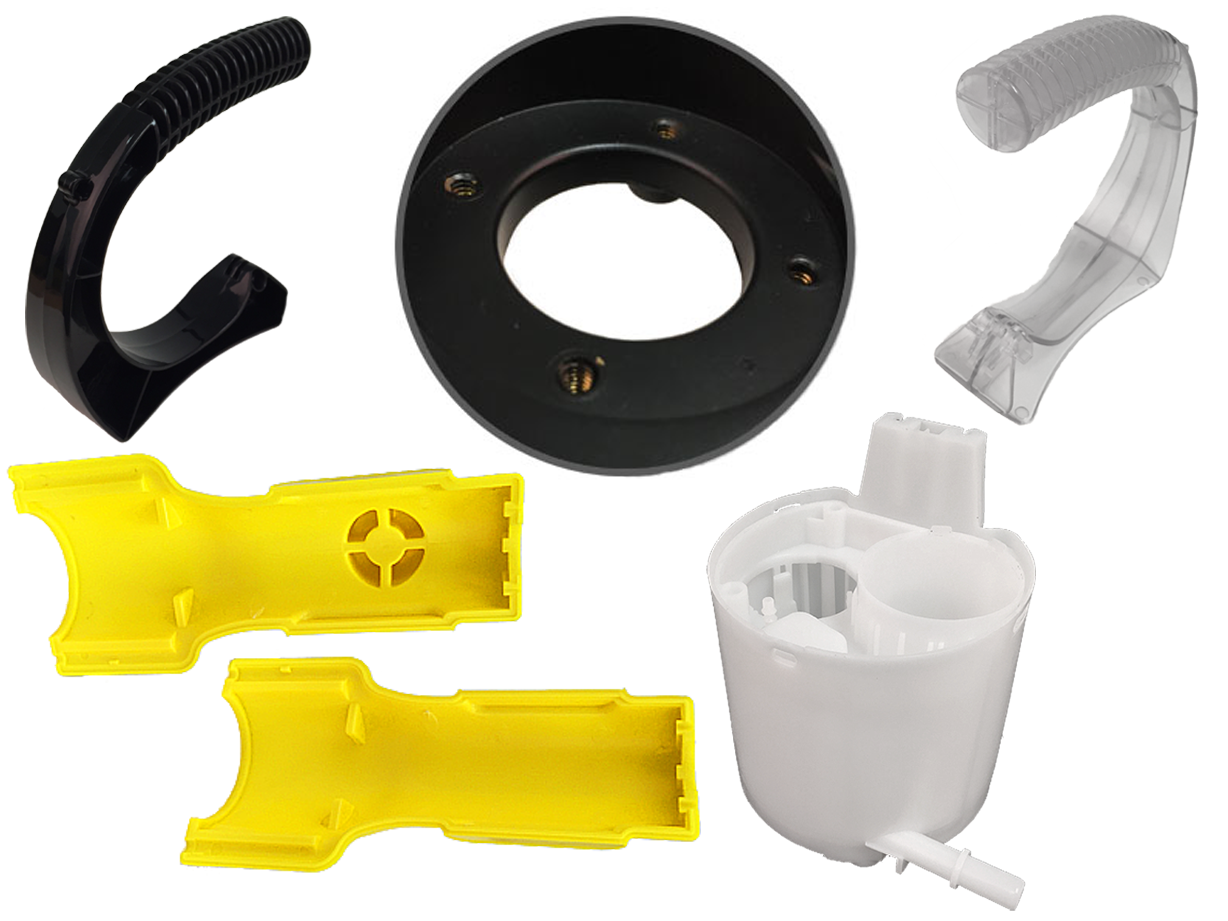 Injection Molded Plastics
Injection Molded Plastics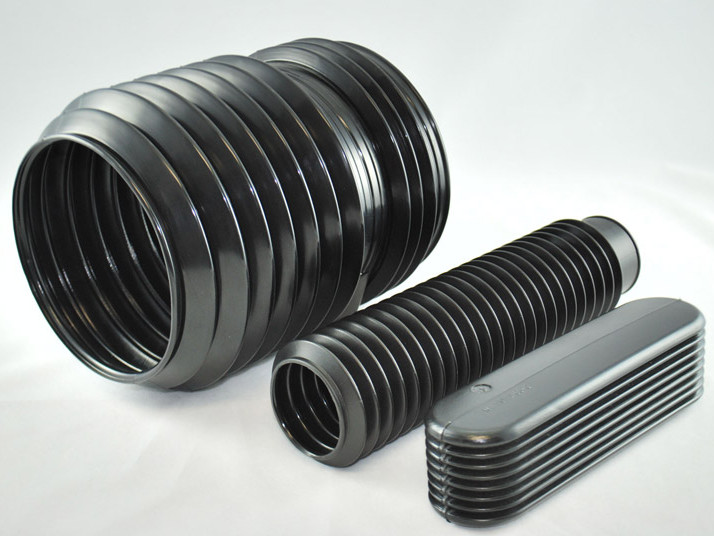 Plastic Blow Molding
Plastic Blow Molding Plastic Dip Molding
Plastic Dip Molding Plastic Extrusions
Plastic Extrusions Plastic Tubing
Plastic Tubing Polyurethane Molding
Polyurethane Molding Rotational Molding
Rotational Molding Vacuum Forming
Vacuum Forming Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services