Plastic coating is the process of dipping or immersing an object in liquid polymers or plastic to apply it to its surface. A finished product is dipped into a liquid polymer and completely (or partially) covered in plastisol. The result is a thick plastic finish for aesthetic and protective purposes, increasing the material’s resilience to abrasions, wear, corrosion, and the elements. Read More…
Precision Dip Coating provides dip coating services for the manufacture of soft plastic parts such as cap plugs. hand grips, and more. Decorative and protective, our services are very cost effective and we have a proven track record for on time delivery and precise manufacturing. We can match any color you need, and offer services such as assembly, die cutting, packaging, and decorating.
Carlisle Plastics is a dip molding plastics manufacturer offering end caps, plastisol paint masks, thread protectors, tube closures, protective caps and decorative caps.

At Production Sciences, Inc., we pride ourselves on being pioneers in the realm of dip-molded plastics, sculpting a legacy of innovation and excellence that spans decades. As a collective force, we embody a commitment to precision, creativity, and unwavering quality in the realm of plastic manufacturing.

Innovative Coatings is a manufacturer of plastisol dip molding and fluidized bed powder coatings of epoxy, polyolefins, nylon and vinyl. Our dip coatings are of FDA-approved and biomedical grades.
More Plastic Coating Companies
What is Plastic Coating? Uses, Benefits, and Applications
Plastic coating is a versatile industrial process that increases the tensile strength, durability, and service life of metal objects and components. By applying a protective plastic layer, manufacturers enhance product performance—delivering improved corrosion resistance, mechanical protection, and insulation properties. Plastic coating is widely used across numerous industries, from automotive and aerospace to electronics, construction, and consumer goods.
The process not only boosts mechanical properties but also provides comfort and safety for end users. For example, plastic coatings offer non-slip grips and thermal insulation on hand tools, tongs, and spatulas—ensuring a safer, more ergonomic user experience, especially when handling hot or electrically active items. In electrical engineering, plastic coverings are critical for insulating wires, cables, circuit boards, and digital meter probes, where they help prevent electrical shorts and enhance safety.

Types of Plastic Coating Polymers: Materials & Properties
Selecting the right plastic coating material is essential for optimal product performance and longevity. The most common plastic coating polymers include:
Latex
Latex coatings use a thin emulsion of polymer particles, typically 30-40% rubber. Latex, available as both natural and synthetic rubber, delivers excellent flexibility, grip, and insulation properties—making it popular for protective gloves, tool handles, and laboratory equipment. However, natural latex can trigger allergies in some users, especially if the coating degrades into powder.
Key Benefits: Cost-effective, flexible, easy to apply, good electrical insulation, soft touch.

Plastisol
Plastisol is the most widely used polymer for dip molding and dip coating applications. Composed of fine polyvinyl chloride (PVC) resins suspended in a liquid plasticizer, plastisol forms a soft, flexible, rubber-like coating when heated. The material then returns to a liquid state upon cooling, offering manufacturing flexibility.
The exceptional toughness, corrosion resistance, and impact resistance of plastisol coatings make them ideal for harsh industrial environments and electrical insulation applications, thanks to their high dielectric strength. Colorants can be added to tailor the appearance and finish for specialized applications, such as tool grips, medical devices, automotive parts, and outdoor furniture.
Common Uses: Tool handles, grips, caps, dip-molded gloves, wire insulation, marine hardware, sporting goods.
Epoxy
Epoxy coatings are thermosetting polymers that create extremely strong, chemically resistant, and thermally robust surfaces once cured via cross-linking. Epoxy-based plastic coatings are ideal for corrosive environments, chemical processing equipment, pipelines, automotive chassis, and appliance parts.
Advantages: Superior chemical resistance, high strength, excellent adhesion, long lifespan, resistance to heat and abrasion.
Polyurethane
Polyurethane coatings feature carbamate linkages, providing unmatched adaptability and deformation resistance. The balance of flexibility and elasticity makes polyurethane ideal for flexible hoses, conveyor rollers, seals, and custom-molded parts exposed to repetitive movement or mechanical stress.
Benefits: High abrasion resistance, flexible yet tough, oil and chemical resistance, excellent impact absorption.
Neoprene
Neoprene coatings are produced by polymerizing chloroprene, resulting in a synthetic rubber alternative to latex. Neoprene is prized for its outstanding elasticity, chemical resistance, and weatherproofing properties, making it popular for gaskets, protective covers, cable jackets, and marine applications.
Key Features: Resistant to oils, ozone, sunlight, and many chemicals; maintains flexibility in extreme temperatures.
Plastic Coating Process: How Does It Work?
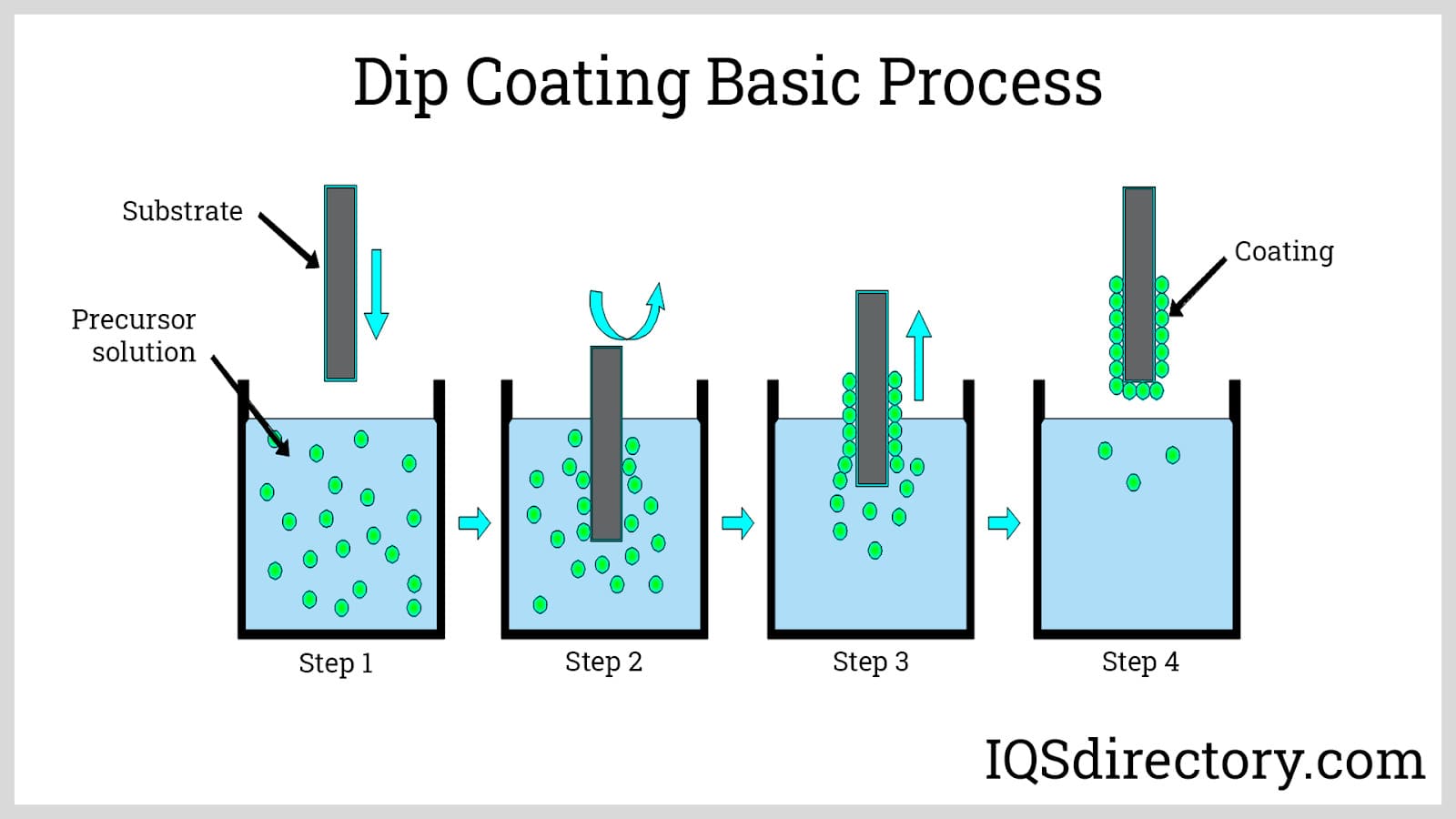
The plastic coating process refers to a family of industrial techniques for applying a protective plastic layer to metal, glass, or other substrate materials. The most common technique is dip coating (dip molding), which allows manufacturers to achieve uniform coating thickness and high production efficiency.
Step-by-Step Plastic Dip Coating Process:
- Preparation: The substrate (often metal or wire) is cleaned of contaminants and debris to ensure optimal adhesion.
- Preheating: The item is heated to a specific temperature, which encourages the molten or liquid polymer to bond tightly.
- Immersion: The preheated part is submerged (dipped) into the chosen plastic or polymer solution, such as plastisol, latex, or neoprene.
- Withdrawal: The coated part is slowly withdrawn at a controlled rate to ensure even coverage and desired coating thickness.
- Curing: The coated item is heated further or allowed to cool, depending on the polymer, to solidify, cross-link, and permanently bond the coating.
- Finishing: Post-processing steps, such as trimming, deflashing, or surface texturing, may be performed for a precise finish.
Dip molding and dip coating are similar, with dip molding producing hollow or double-walled items like latex gloves, medical balloons, bellows, and tubing. By contrast, dip coating is primarily used for applying protective layers to solid objects. This process minimizes raw material waste by reducing subtractive machining and secondary finishing operations.
Typical Dip-Molded Products: Gloves, costume accessories, laboratory ware, electrical connectors, cable end caps, and recreational equipment.

Advantages of Plastic Coating: Why Choose This Solution?
- Vibration Damping: Heavy machinery and industrial equipment naturally generate vibrations, which can lead to premature wear and mechanical failure. Plastic coatings act as vibration dampeners, reducing machine-to-machine contact and extending equipment lifespan.
- Noise Reduction: High noise levels are a major challenge in manufacturing and processing facilities. By serving as separators, gaskets, shields, and enclosures, plastic coatings effectively absorb sound and lessen ambient noise, creating safer and more comfortable working environments.
- Friction Reduction: Excessive friction can damage equipment and decrease operational efficiency. A plastic coating applied to moving parts reduces friction, minimizing wear, abrasion, and electromagnetic interference. This leads to smoother, more reliable operation and lower maintenance costs.
- Insulation: Plastic coatings serve as robust electrical and thermal insulators. They protect workers and sensitive components from electrical shock, static discharge, and heat, while also preventing metal-on-metal contact and reducing electromagnetic fields (EMFs).
- Corrosion Resistance: By providing a moisture-resistant barrier, plastic coatings protect metal substrates from corrosion, rust, and chemical attack. This is especially beneficial in marine, chemical processing, and outdoor environments.
- Customization: Plastic coating processes allow for a wide range of thicknesses, colors, textures, and finishes. This flexibility enables manufacturers to tailor products for specific branding, safety, and functional requirements.
- Cost Savings: Durable plastic coatings minimize the need for frequent replacements, reduce downtime, and lower total cost of ownership by preserving core equipment and extending product lifecycles.
Applications for Plastic Coating: Industries & End-Use Scenarios
Plastic coating is a critical solution across a wide variety of industries and product categories. Common applications include:
- Automotive: Wiring harnesses, battery terminals, underbody components, and brake lines benefit from plastic coatings for enhanced corrosion resistance, insulation, and noise reduction.
- Electrical & Electronics: Insulation of wires, connectors, switches, circuit boards, and sensor housings protects against electrical faults and environmental hazards.
- Medical Devices: Catheters, surgical instruments, grips, and tubing require biocompatible, easy-to-clean, and chemically resistant plastic coatings.
- Construction: Fencing, handrails, fasteners, rebar, and architectural hardware are coated for improved weatherproofing and safety.
- Industrial Equipment: Valves, pumps, conveyor rollers, and machine guards are protected from abrasion, chemicals, and mechanical shock.
- Consumer Goods: Tool handles, kitchen utensils, sporting goods, and recreational equipment feature ergonomic, slip-resistant coatings for safety and comfort.
- Marine: Boat parts, dock hardware, cables, and chains are plastic coated to resist saltwater corrosion and UV degradation.
- Aerospace: Lightweight, high-performance coatings shield components from extreme temperatures, chemicals, and vibration.
Are you looking for a specific use case or application?
Explore our industry guides or contact our plastic coating experts to discuss your unique project requirements.
Plastic Coating vs. Powder Coating: Which Is Right for Your Project?
When selecting a surface protection method, buyers often weigh plastic coating against powder coating. Both offer robust protection, but their properties, applications, and benefits differ:
- Plastic Coating: Flexible, thicker, and excellent for electrical insulation and impact absorption. Ideal for parts that require grip, flexibility, and weather resistance.
- Powder Coating: Hard, thin, and highly durable. Best for decorative finishes and applications requiring abrasion and UV resistance but not flexibility.
Need help choosing between plastic coating and powder coating?
Ask our experts or visit our in-depth comparison guides for detailed insights.
Buyer’s Guide: How to Select the Right Plastic Coating Company
Choosing the right plastic coating supplier or manufacturer is crucial for ensuring quality, consistency, and value. Consider the following decision factors when evaluating plastic coating companies:
- Material Expertise: Does the company offer the specific polymer (plastisol, latex, polyurethane, epoxy, neoprene) that matches your application needs?
- Production Capabilities: Can they handle your order volume, part sizes, and specialized requirements (e.g., color matching, custom finishes, rapid prototyping)?
- Industry Certifications: Look for ISO, FDA, or other relevant certifications for medical, food-grade, or safety-critical applications.
- Quality Assurance: What quality control processes are in place? Ask about sample testing, inspection, and traceability measures.
- Lead Time & Logistics: Can the supplier meet your delivery deadlines? Inquire about minimum order quantities, shipping, and packaging options.
- Customer Support: Responsive technical support, transparent communication, and ongoing service are crucial for long-term partnerships.
Ready to compare plastic coating providers?
Use our plastic coating company directory to browse suppliers, view detailed business profiles, and request quotes using our easy RFQ form.
Frequently Asked Questions about Plastic Coating
- What are the most common types of plastic coatings?
Plastisol, latex, polyurethane, epoxy, and neoprene are widely used, each offering unique benefits for specific applications. - How thick can plastic coatings be applied?
Thickness ranges from a few microns to several millimeters. The ideal thickness depends on the polymer type and end-use requirements. - Is plastic coating environmentally friendly?
Many coatings are formulated for low VOC emissions and recyclability. Biodegradable and eco-friendly options are increasingly available—ask your supplier about sustainable choices. - Can plastic coating be applied to surfaces other than metal?
Yes. While metal is common, glass, ceramics, and some plastics (with proper surface treatment) can also be coated. - What is the expected lifespan of a plastic coating?
With proper application and material selection, plastic coatings can last for years—even decades—in harsh environments. - How do I maintain or repair a damaged plastic coating?
Minor chips or abrasions can often be repaired on-site using patch kits or re-coating. For extensive damage, professional recoating is recommended.
Find a Plastic Coating Company Near You
For the most beneficial outcome when selecting a plastic coating company, it is important to compare several companies using our directory of plastic coating businesses. Each plastic coating company has a business profile page highlighting their areas of experience and capabilities, along with a contact form to directly communicate with the business for more information or request a quote. Review each plastic dip coating company website using our patented website previewer to gain a better understanding of what each business specializes in. Then, use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple plastic coating companies with the same form.
Looking for a trusted partner for your next coating project?
Start your search now, or contact our experts for recommendations based on your application, industry, and technical requirements.
Get Expert Guidance on Your Plastic Coating Project
Not sure where to start or which plastic coating process best fits your needs? Our network of industry experts is ready to help. Whether you need advice on material selection, process optimization, regulatory compliance, or supplier vetting, we offer tailored guidance to ensure your project’s success.
Ask an expert:
- What’s the most cost-effective plastic coating for outdoor equipment?
- How do I ensure FDA or food-safe compliance for coated products?
- What are best practices for coating complex or irregularly shaped parts?
- How can I maximize abrasion and chemical resistance for industrial coatings?
Contact us today to schedule a consultation or get a quote for your custom plastic coating project.





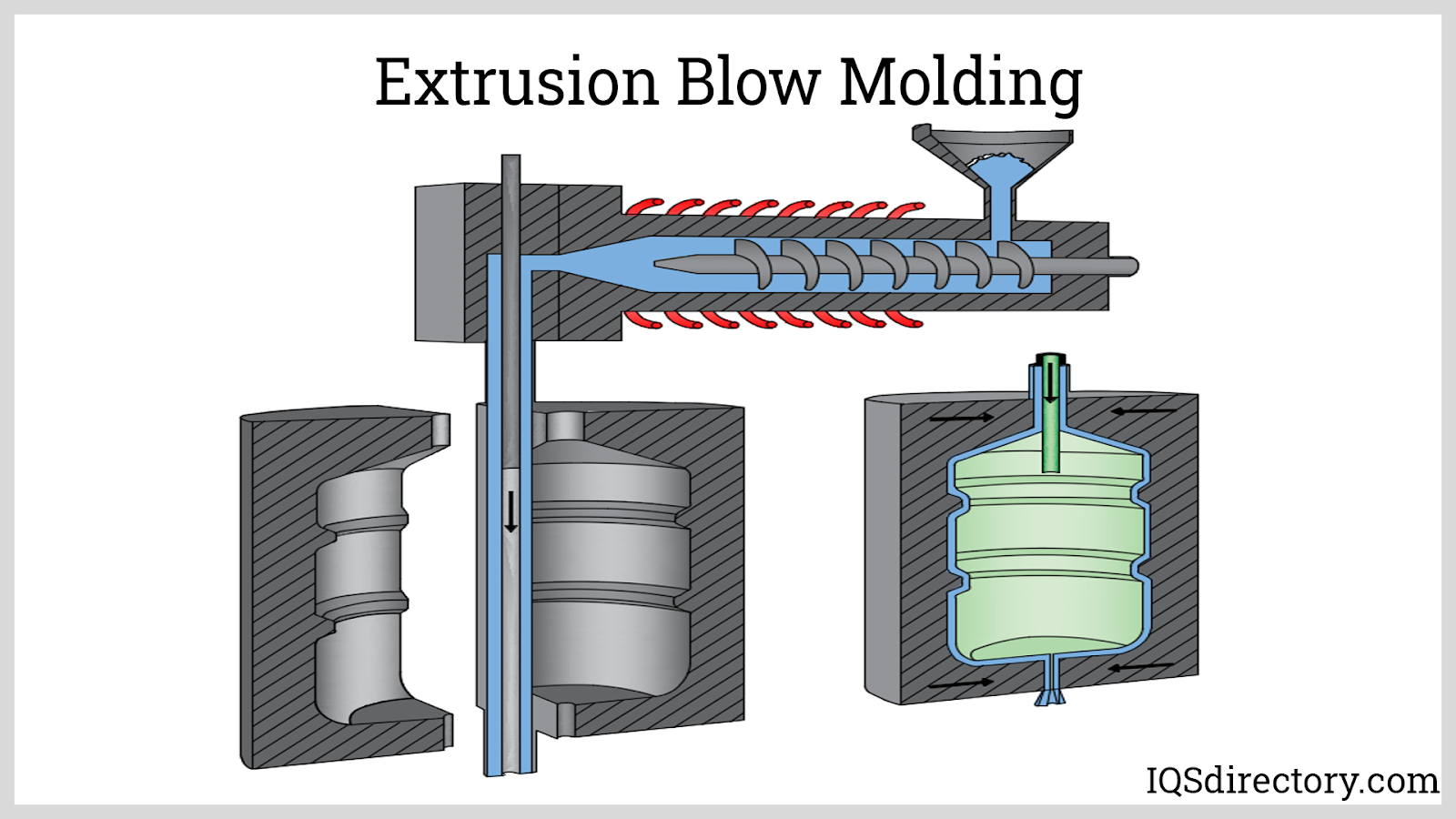

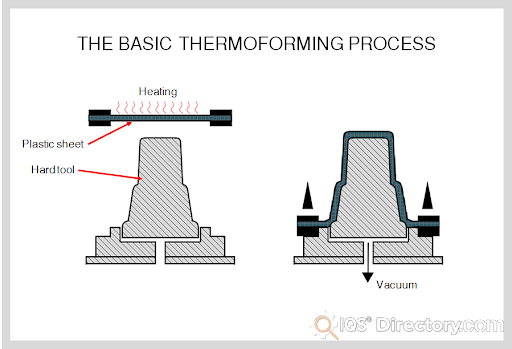
 Fiberglass Fabricators
Fiberglass Fabricators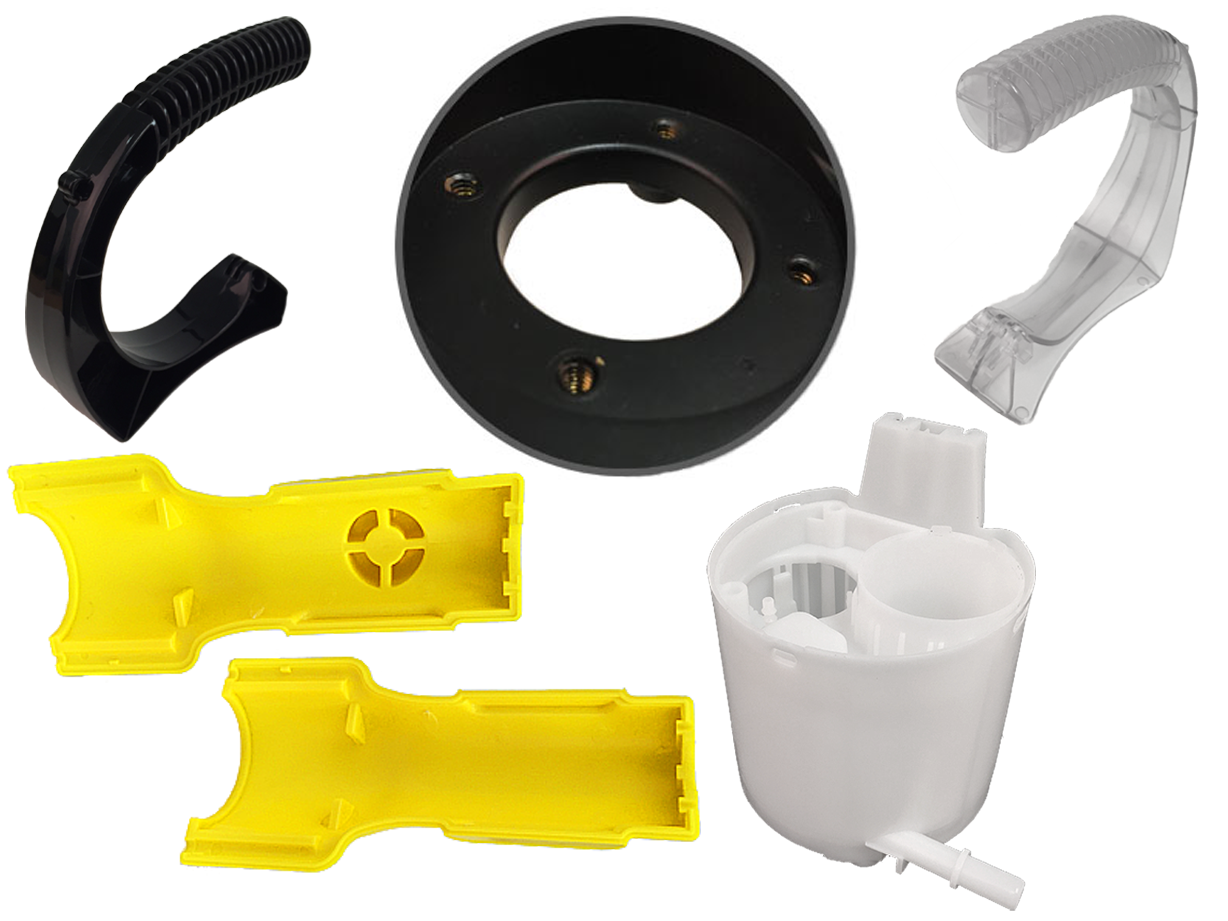 Injection Molded Plastics
Injection Molded Plastics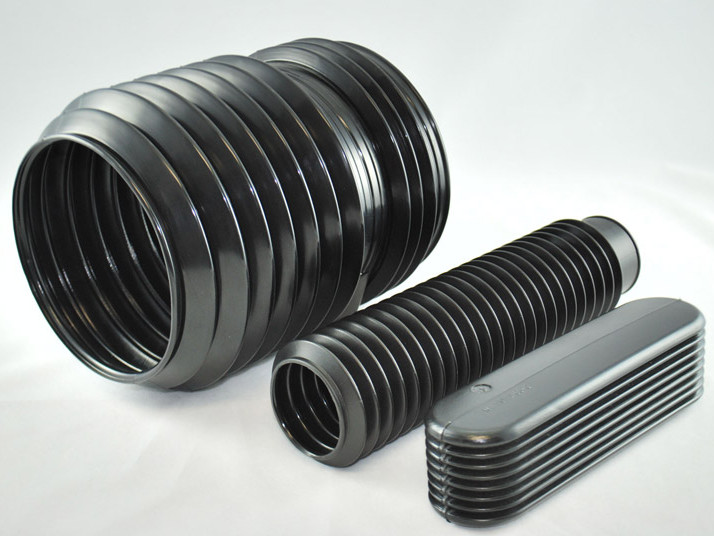 Plastic Blow Molding
Plastic Blow Molding Plastic Dip Molding
Plastic Dip Molding Plastic Extrusions
Plastic Extrusions Plastic Tubing
Plastic Tubing Polyurethane Molding
Polyurethane Molding Rotational Molding
Rotational Molding Vacuum Forming
Vacuum Forming Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services